Mixture models in general dont require knowing which subpopulation a data point belongs to allowing the model to learn the subpopulations automatically. 13-MoG 2 33.
Sklearnmixture is a package which enables one to learn Gaussian Mixture Models diagonal spherical tied and full covariance matrices supported sample them and estimate them from data.
. Instead of estimating the mean and variance for each Gaussian now we estimate the mean and the covariance. One visual analogy I found particularly useful is imagining Gaussians as some sort of hill or mountain on a contour map. 11 Motivation and Related Work.
Gaussian Mixture Model or Mixture of Gaussian as it is sometimes called is not so much a model as it is a probability distribution. To build a good model it is. It runs in time only linear in the dimension of the data and polynomial in the number of Gaussians.
For instance here is a mixture of 25 N 2 1 and 75 N 2 1 which you could call one part N 2 1 and three parts N 2. The conditional distribution p y x. Remember the density function of the Gaussian mixture model.
Centers of the Gaussians to within the precision specified by the user with high probability. 1 Introduction The mixture of Gaussians is among the most enduring well-weathered models of applied statistics. Each Gaussian would have its own mean and variance and we could mix them by adjusting the proportional coefficients pi.
A Gaussian mixture of three normal distributions. Sample from gaussian 2. The GaussianMixture API in this package implements the expectation-maximization EM algorithm to estimate the parameters of the Gaussians in the mixture model.
It is particularly well suited to describe data containing clusters. Generative models explanation or prediction inference. Gaussian mixture regression can be used to predict distributions of variables y by computing.
This is achieved by using the SGMM as a likelihood function. It has five parameters. The covariance is a squared matrix of shape D D where D represents the data dimensionality.
A mixture distribution combines different component distributions with weights that typically sum to one or can be renormalized. Facilities to help determine the appropriate number of. The conditional distribution of.
A Generative View of Clustering. Gaussian Mixture Models for 1D data using K equals 2. Sample from gaussian 1 return statsnormrvs3507 else.
Approximate density with a mixture of Gaussians Sham Kakade 2016 6. An example of a univariate mixture of Gaussians model. Erly chosen statistical generative model for the data under consideration.
We simply restricted the generative model to exhibit a specific behavior which indirectly led to the modified-M2 deciding that having 10 different data-generating manifolds is a good thing. We first sample a value between 0 and 1 and pick the normal. Olshausen November 1 2010 The mixture of Gaussians model is probably the simplest interesting example of a generative model that illustrates the principles of inference and learning.
Gaussian Mixture Models Permalink. 1 Gaussian mixture models are a probabilistic model for representing normally distributed subpopulations within an overall population. It is also called Expectation-Maximization Clustering or EM Clustering and is based on the optimization strategy.
Mixture of Gaussians EM algorithm Latent Variables Zemel Urtasun Fidler UofT CSC 411. One first generates a discrete variable that determines which of the component Gaussians to use and then generates an observation from the chosen density. Generative model I Then we adjust the model parameters to maximize the probability that it would produce exactly the data we observed Zemel Urtasun Fidler UofT CSC 411.
Maximum Likelihood and Maximum a Posteriori The model parameters θ that make the data most probable are called the. Surprisingly we made no change to the inference model at all. A gaussian-mixture is the special case where the components are Gaussians.
The motivating idea behind GMMs is that we can model seemingly complicated distributions as a convex combination of Gaussians each defined by different parameters. Gaussian mixture models. It has the following generative process.
However the figures got mixed up. 13-MoG 3 33. Each cluster is represented by a Gaussian kernel the whole collection thus makes up a mixture of Gaussians which we will call a Simplex Gaussian Mixture Model SGMM.
The Real Gaussian. Mixture model formulation Generative model Likelihood Expectation Maximization EM Algorithm Derivation. It is a universally used model for generative unsupervised learning or clustering.
The mixture of Gaussians model Bruno A. Generative Code from scipy import stats def sample. Building up to the Mixture of Gaussians Single Gaussians Fully-Observed Mixtures Hidden Mixtures.
You have to use a non-degenerate mixture of Gaussians or I will cut you. The mixture was initialized randomly in two different ways and run for three iterations based on each initialization. Choose group membership membership statsbernoullirvs02 if membership 1.
We estimated a mixture of two Gaussians based on two rdimensional data shown below. For vector data there are well studied clus-tering algorithms for popular generative models such as a mixture of Gaussians whose e ect is analogous to the use of Euclidean or Mahalanobis type distances from the dis-criminative perspective. A mixture of Gaussians is best described in terms of the generative model.
Something like this is known as a Gaussian Mixture Model GMM. Each of the clusters draw embeddings of fake images towards their center. With probability 07 choose component 1 otherwise choose component 2 If we chose component 1 then sample xfrom a Gaussian with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
This would be like mixing different sounds by using the sliders on a console. Gaussian mixture models scikit-learn 102 documentation. 4 to describe the two gaussians and one to describe the relative weighting of the two gaussians.
Generative Models Generative models Modeling the joint probabilistic distribution of data Given some hidden parameters or variables Then do the conditional inference Recover the data distribution essence of data science Benefit from hidden variables modeling Eg. Please draw an arrow from one figure to another to indicate how they follow from. Figure 2 shows an example of a mixture of Gaussians model with 2 components.
For high-dimensional data D1 only a few things change. Here is an idea what if we use multiple Gaussians as part of the mixture. The pis can be seen as the strength of the corresponding Gaussian.
Gaussian Mixture Model Sham Kakade 2016 3. Naive Bayes Hidden Markov Model Mixture Gaussian Markov.
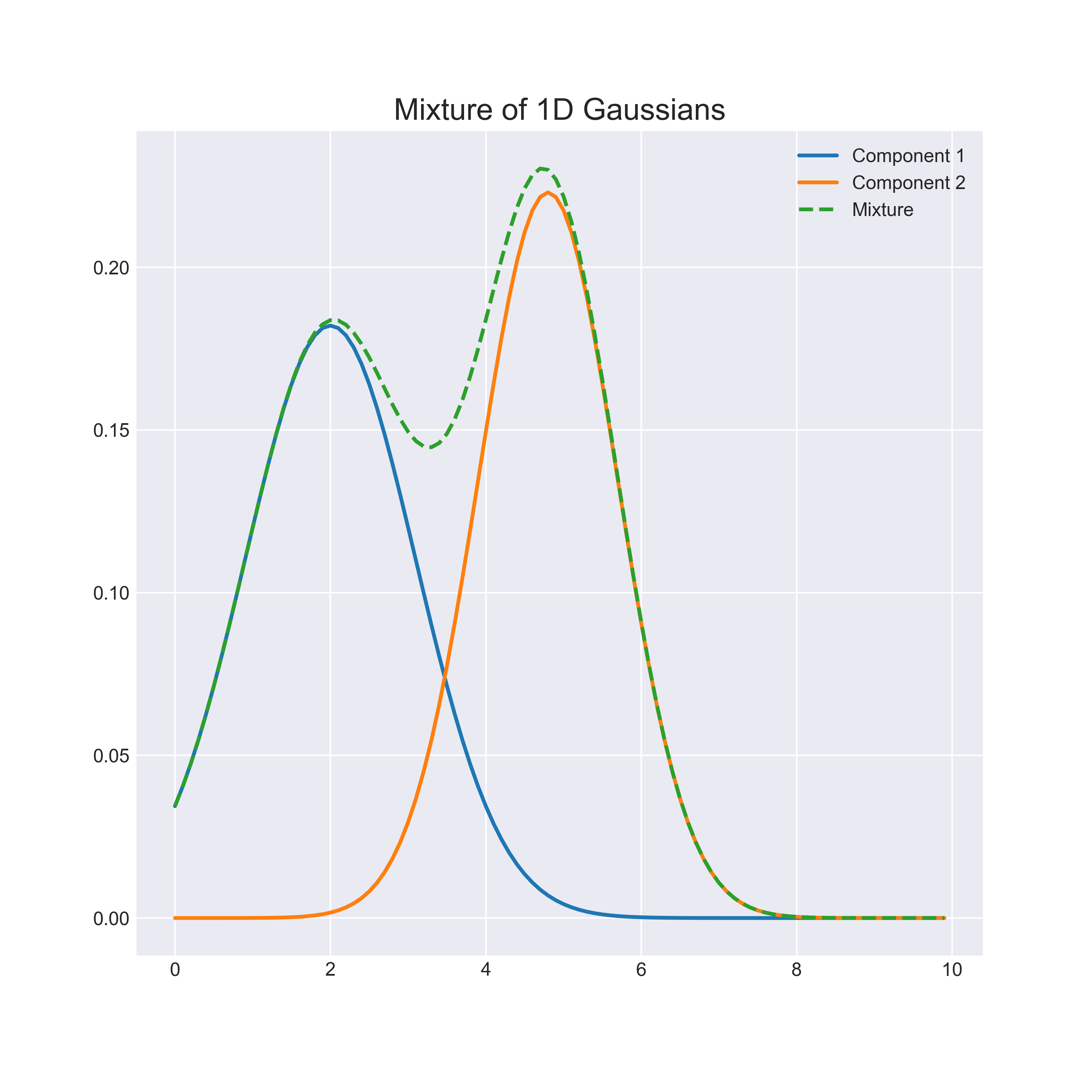
Gaussian Mixture Models In Pytorch Angus Turner
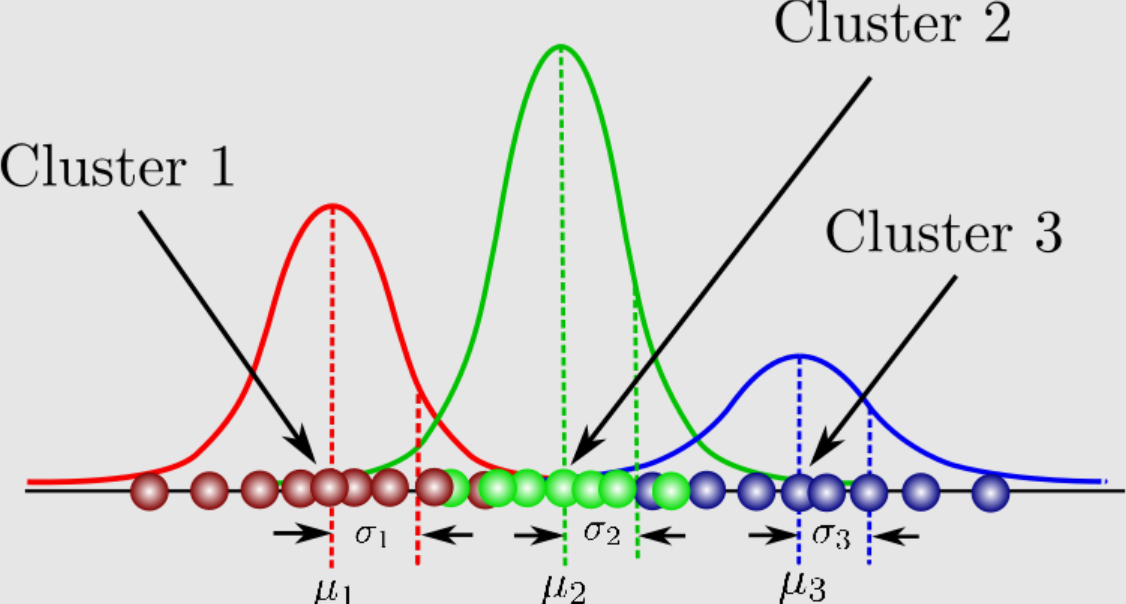
Gaussian Mixture Models What Are They When To Use Data Analytics
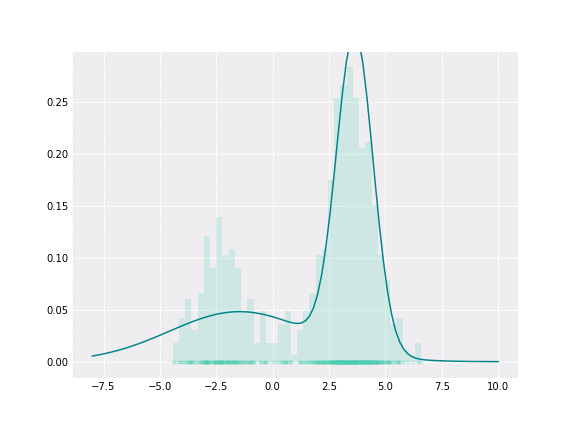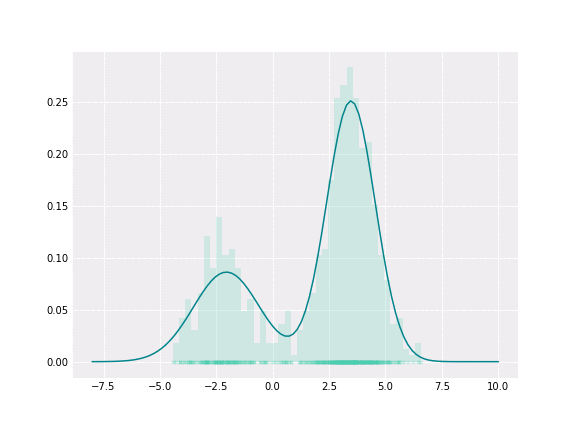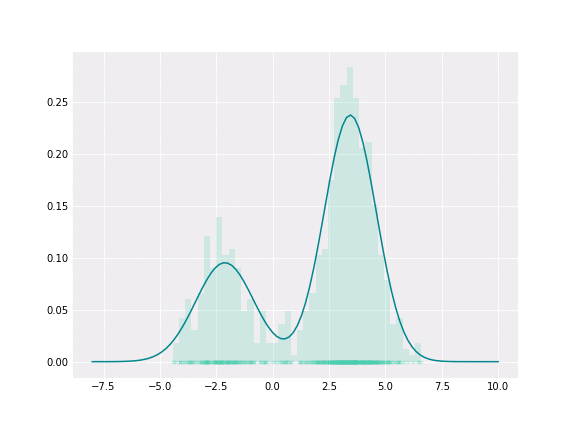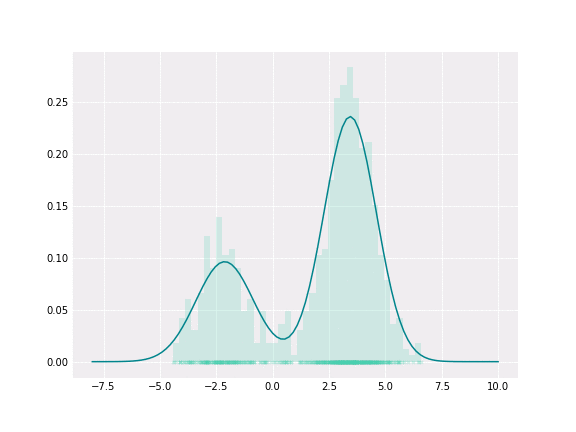
Gaussian Mixture Models Visually Explained Anastasia Kireeva S Blog
0 Comments